The almond tree (Prunus dulcis) is one of the most important fruit trees in temperate and semi-arid regions of the world. With its relative tolerance to drought, adaptability to low-fertility soils, and high economic value of its fruit, almond has gained a special place in horticulture. Iran, as one of the main almond producers in the world, annually produces and exports thousands of tons of almonds. Therefore, choosing the right time for planting almond seedlings and managing the orchard properly are key factors for achieving high and profitable yields.
One of the main questions farmers often ask when establishing an almond orchard is: When is the best time to plant almond trees? The answer depends on the climatic conditions of the region, the type of seedling, and the planting method. In this article, we will not only discuss the best time for planting but also provide practical tips for successful orchard establishment.
Factors Affecting the Planting Time of Almond Trees
The timing of almond planting depends on several important factors:
-
Climatic Conditions
Almond trees require mild winters and hot summers. Extremely low temperatures and late frosts can damage blossoms or even freeze the roots. Therefore, planting time must be carefully chosen according to local weather conditions. -
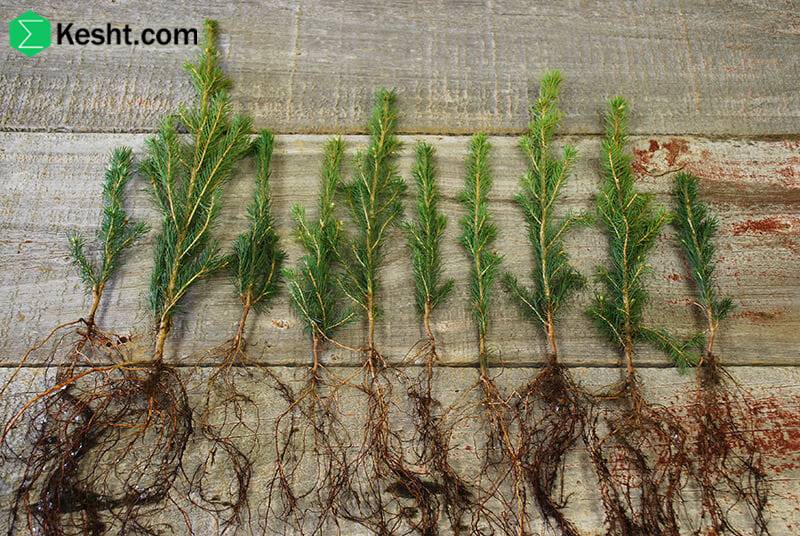
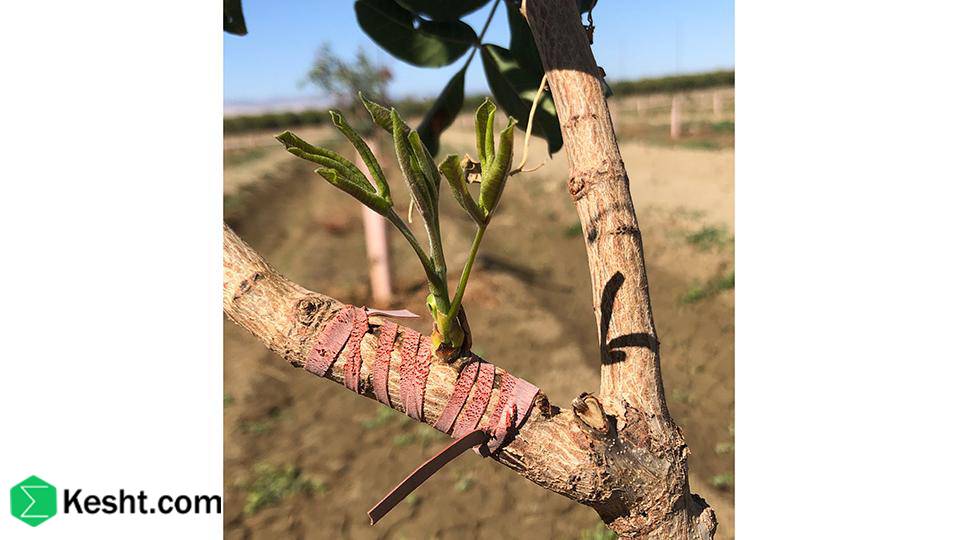
Type of Seedling
-
Bare-root seedlings: These must be planted during dormancy (late autumn to winter).
-
Containerized seedlings: These come with soil around their roots and can be planted throughout the year, except during extremely hot and dry periods.
-
-
Soil and Moisture Conditions
The soil should have a medium texture (loamy or sandy-loam), good drainage, and sufficient depth. Excessively wet soil at planting can suffocate the roots, so moisture levels must be carefully considered.
The Best Time to Plant Almond Trees
Based on farmer experience and scientific recommendations, the best planting windows are:
-
Late Autumn (November to early December)
In areas with mild winters, this is the ideal time. Seedlings have enough time to adapt and establish before the severe cold arrives, and they start growing quickly in spring. -
Mid-Winter (January to February)
In colder areas, it is better to wait until mid- or late winter to reduce the risk of root freezing. -
Early Spring (March to early April)
In regions with long and harsh winters, early spring is the best time—just before hot and dry weather begins. This allows seedlings to establish quickly and avoid frost damage.
Practical Tips for Successful Planting
1. Land Preparation
-
Deep plowing in summer or early autumn improves soil aeration and drainage.
-
Applying well-rotted manure (20–40 tons per hectare) before planting enriches the soil.
-
In calcareous or saline soils, adding organic matter and soil amendments such as sulfur or gypsum is recommended.
2. Choosing the Right Seedling
-
Always buy seedlings from certified nurseries under the supervision of agricultural authorities.
-
Rootstocks resistant to drought or diseases (such as GF677 or bitter almond seedling rootstocks) are better choices for certain areas.
-
Healthy seedlings should have strong, undamaged roots and be free from pests and diseases.
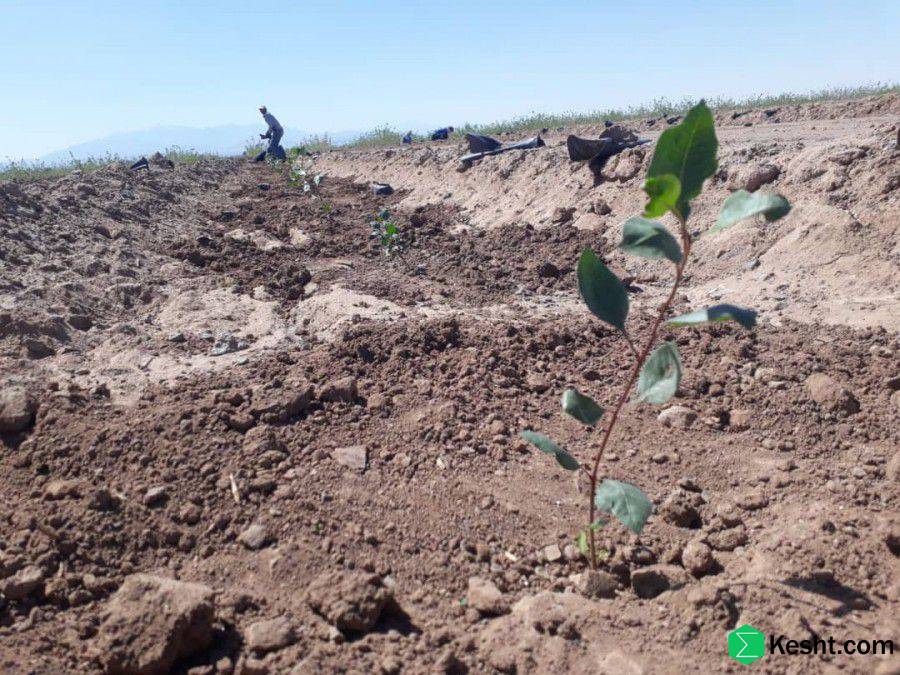
3. Preparing the Planting Hole
-
Dig planting holes about 60 × 60 × 60 cm.
-
Keep the topsoil and subsoil separate, and place the enriched topsoil mixed with organic matter at the bottom of the hole.
-
Add sand or leaf mold if necessary to improve aeration.
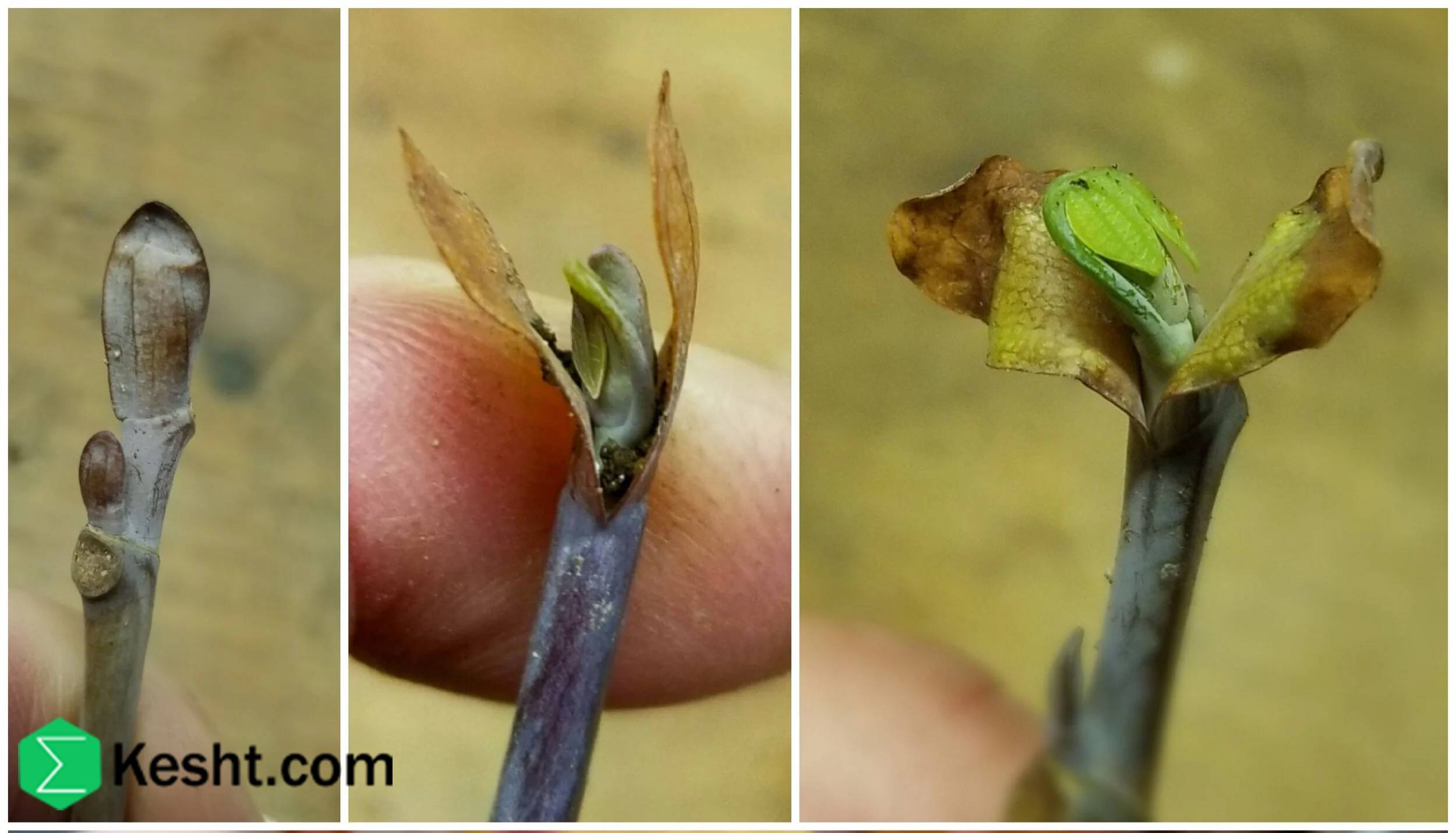
4. Proper Planting Method
-
The roots must be fully covered with soil, without leaving air pockets around them.
-
Water the seedling immediately after planting to settle the soil around the roots.
-
Use a stake to support the young tree against wind damage.
Post-Planting Care
Planting is only the first step; careful management afterward is crucial:
-
Irrigation: During the first year, frequent light irrigation is essential. In dry areas, drip irrigation is highly recommended.
-
Pruning: Initial formative pruning should be done after planting or within the first year to create a strong tree framework.
-
Frost Protection: In cold winters, temporary covers or mulching can protect the trunk and roots from freezing.
-
Pest and Disease Control: Winter spraying with dormant oil and copper-based compounds before bud break helps reduce early pest and disease pressure.
Local Experiences in Almond Planting
Farmers in different regions of Iran have developed local practices for better results:
-
In arid areas, autumn planting is preferred so seedlings can benefit from winter rainfall and reduce irrigation needs.
-
In cold regions such as Hamedan or Chaharmahal, farmers often delay planting until early spring to avoid late frosts.
-
In warmer southern regions like Fars or Kerman, autumn planting usually gives the best results.
Conclusion
Choosing the right time for planting almond trees is a key factor for successful orchard establishment and higher economic returns. In summary:
-
In mild climates: autumn planting is best.
-
In cold climates: early spring planting is safer.
-
In dry regions: autumn planting helps seedlings use natural rainfall.
In addition, proper land preparation, selecting healthy seedlings, following correct planting methods, and post-planting care are essential for ensuring good growth and high productivity. By following these principles, farmers can achieve rapid establishment and look forward to a prosperous and fruitful orchard in the years to come.