Introduction
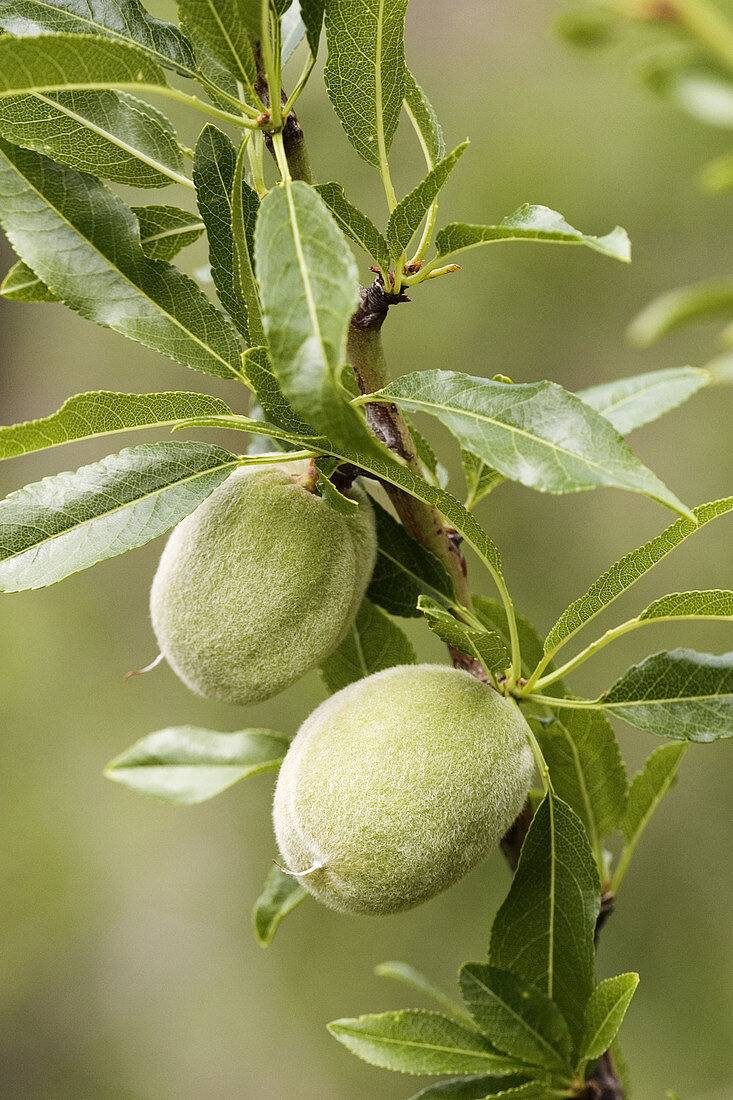
The almond tree (Prunus dulcis) is one of the most valuable and economically important fruit trees in Iran and many parts of the world. Due to its high nutritional value, strong market demand, relative drought tolerance, and profitability, almond cultivation has been increasing in many regions.
However, one critical factor that is often overlooked is that the success of an almond orchard largely depends on the initial choice of saplings. A carefully selected sapling lays the foundation for years of productivity and profitability. Conversely, poor-quality or unsuitable saplings can cause irreparable losses to growers.
This article explores the key criteria for choosing the best almond saplings, important considerations when buying, and the role of guaranteed saplings in ensuring success.
Why Choosing the Right Almond Sapling Matters
Unlike seeds, saplings have a defined genetic makeup that determines fruit quality, yield, and environmental resistance. Proper selection of saplings brings several advantages:
-
Faster fruit-bearing and earlier entry into the productive phase.
-
Higher resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses.
-
Better quality and more marketable nuts.
-
Reduced orchard management and maintenance costs.
Key Criteria for Selecting the Best Almond Sapling
1. Climate Compatibility
Each almond variety has specific climatic requirements. Choosing a sapling suited to the local climate is the most important factor in orchard success.
-
Cold regions: Late-blooming varieties (such as Ferragnes or Texas) are ideal to avoid spring frost damage.
-
Warm or temperate regions: Early- or mid-blooming varieties can be used.
-
Chilling requirements: The variety must match the region’s winter chill hours.
2. Rootstock and Grafting
Almond saplings are usually grafted onto different rootstocks. The right rootstock improves adaptability and resistance:
-
Bitter almond rootstock: High drought tolerance.
-
Peach–almond hybrid (GF677): Vigorous growth, suitable for calcareous soils.
-
Peach rootstock: Less suited to dry areas.
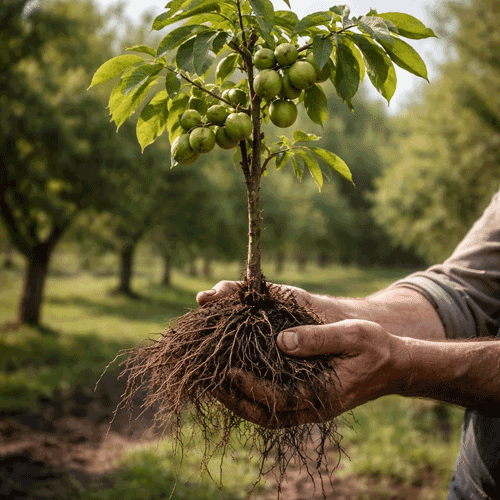
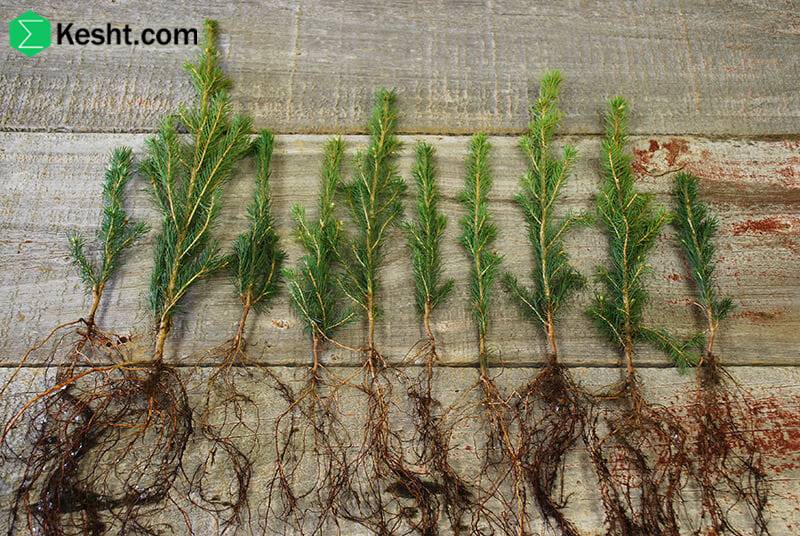
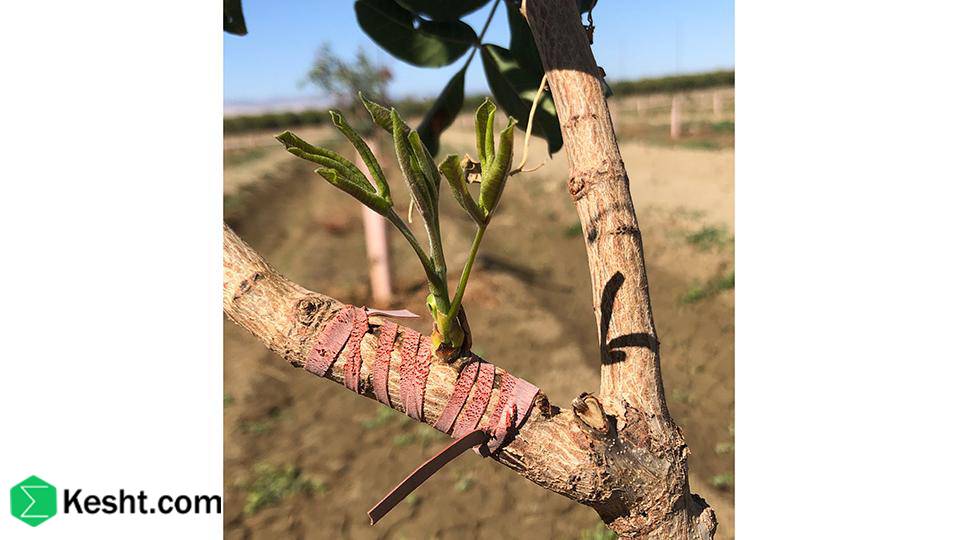
3. Sapling Health and Appearance
Visual inspection can reveal the sapling’s quality:
-
Straight trunk, free of cracks or injuries.
-
Healthy, well-branched roots without signs of rot.
-
Plump, green buds.
-
No visible pests or disease symptoms.
4. Age and Size of Sapling
-
Ideal age: 1–2 years old.
-
Height: around 1–1.5 meters.
-
Trunk thickness: at least as wide as a pencil.
5. Time of Purchase and Planting
-
Purchase: Autumn and winter, when the tree is dormant.
-
Planting: Late autumn to late winter, depending on the local climate.

Key Considerations When Buying Almond Saplings
1. Buy from Certified Nurseries
A common mistake among growers is purchasing saplings from unauthorized sellers. Such saplings often lack authenticity, perform poorly, or may carry hidden pests and diseases.
Certified nurseries usually hold permits from agricultural authorities and provide sapling certificates.
2. Sapling Certificate and Label
Standard saplings must carry a label or certificate with:
-
Variety and rootstock details.
-
Sapling age.
-
Place of production.
-
Plant health and quarantine approval.
3. Inspect the Roots and Trunk
Before purchase, check the roots:
-
Healthy roots should be white and firm.
-
Avoid twisted, dry, or rotten roots.
-
The trunk should be smooth and free of wounds.
4. Choose Marketable and Productive Varieties
Some almond varieties are more profitable due to their nut size, kernel quality, and market demand. In Iran, for example, common commercial varieties include:
-
Ferragnes (late-blooming, high-yield).
-
Texas (frost-resistant, large kernels).
-
Azar and Neyriz (adaptable to various climates).
5. Pollination Requirements
Almonds are generally self-incompatible; many varieties require cross-pollination to set fruit. When buying, growers must plant a combination of compatible varieties to ensure proper pollination.
Common Mistakes When Buying Almond Saplings
-
Purchasing uncertified saplings without identification.
-
Planting early-blooming varieties in cold regions.
-
Choosing older or weak saplings due to lower price.
-
Ignoring rootstock type and suitability.
-
Neglecting cross-pollination requirements.
Guaranteed Saplings: A Safe Choice for Growers
One recent development in the nursery market is the availability of guaranteed saplings. These are produced under strict standards and usually feature:
-
Official certification from agricultural authorities.
-
Verified variety and rootstock authenticity.
-
Full health status, free of pests and diseases.
-
Sometimes replacement guarantees if the sapling fails to match specifications.
Although guaranteed saplings may cost slightly more, they significantly reduce risks and ensure long-term profitability.
Economic Considerations in Choosing Almond Saplings
Establishing an almond orchard is a long-term investment. The chosen sapling must:
-
Be productive and commercially viable.
-
Match both domestic and export market demands.
-
Withstand local challenges such as drought, salinity, or frost.
A poor choice at the beginning can waste years of effort and financial resources.
Conclusion
Selecting the right almond sapling is the first and most crucial step in orchard establishment. A sapling that meets the necessary standards in terms of variety, rootstock, age, health, and authenticity ensures a profitable future. Growers must pay close attention to climate compatibility, orchard pollination needs, and the credibility of the nursery.
Purchasing guaranteed saplings with proper certification and health assurance is the most reliable strategy for reducing risk and securing long-term success. Ultimately, a productive almond orchard always begins with a healthy, high-quality sapling.