Frozen waterlogged swamp soil conditions for seedlings
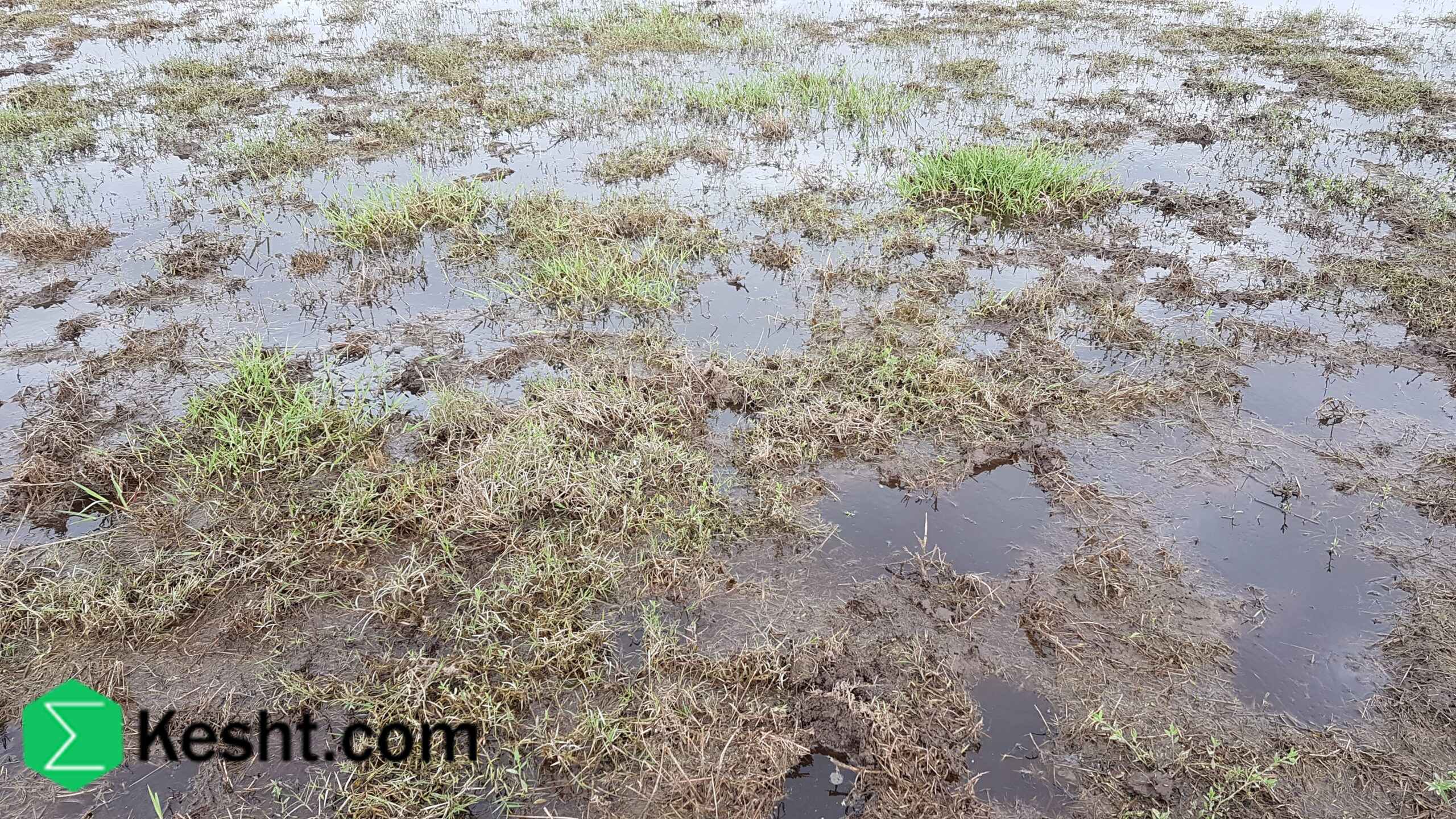
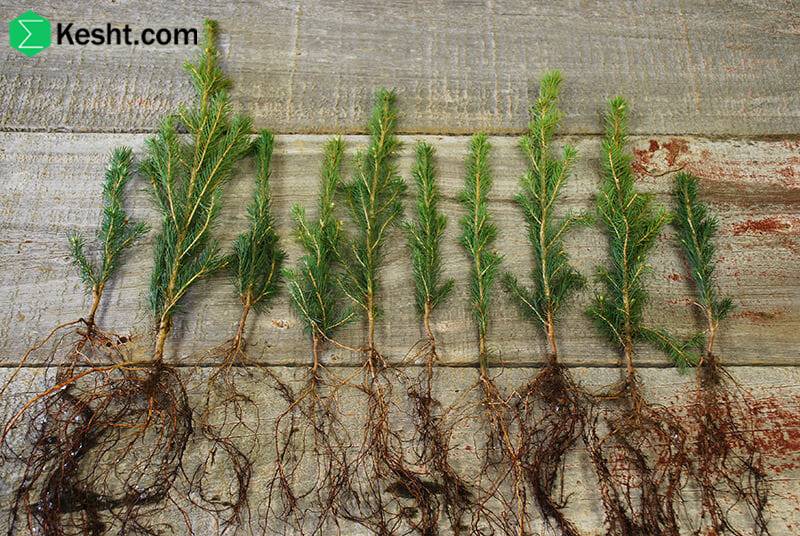
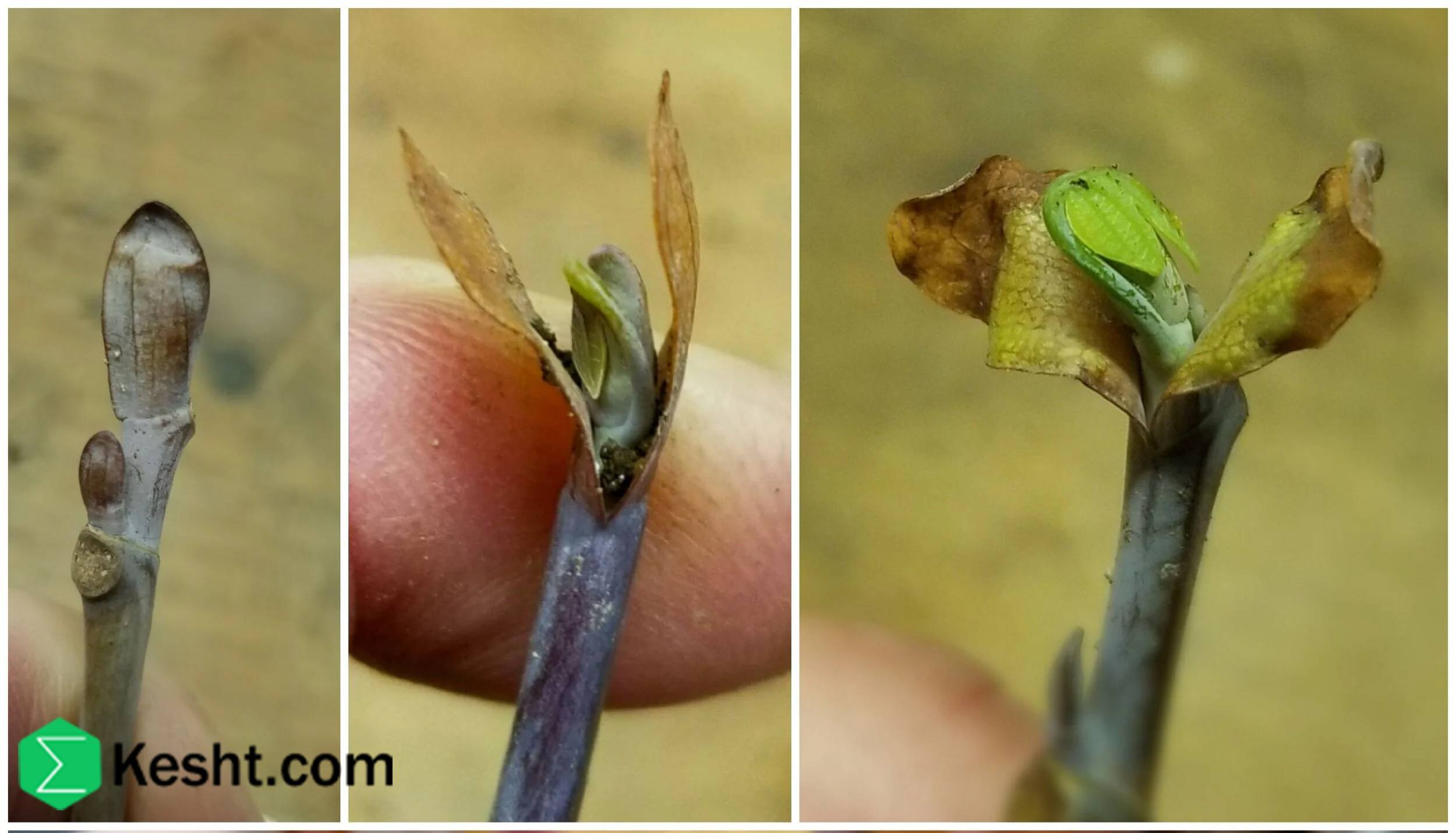
Frozen, waterlogged swamp soil is a challenging environment for planting saplings due to three main factors: being swampy (permanently saturated), waterlogged (high water table), and frozen (below zero temperatures). This combination leads to severe conditions for saplings, resulting in oxygen deficiency, impaired nutrient absorption, root damage from ice, halted root growth, and the risk of winter kill. Swampy soil lacks sufficient oxygen because it remains constantly saturated, causing roots to die despite appearing healthy. When soil is waterlogged, roots are submerged, disrupting their ability to breathe and take in nutrients. Freezing not only stops nutrient movement but also causes physical harm to roots through ice formation. Roots cannot develop in frozen ground, and cold, moist conditions can deplete stored energy, preventing bud growth in spring. Planting in these conditions is possible but requires specific strategies. Choose hardy, native species adapted to cold, wet environments, such as common reed and certain birches. Active soil management is crucial, including improving drainage with ditches and perforated pipes or creating raised planting mounds to elevate saplings above saturated layers. Timing is essential; it’s best to plant in early spring after the thaw and before the soil becomes saturated again. Consider using insulating covers to reduce frost effects and monitor soil conditions continuously. Overall, thorough planning and careful selection can allow successful planting in challenging frozen, waterlogged swamp soils, but without management, saplings face high mortality risks.