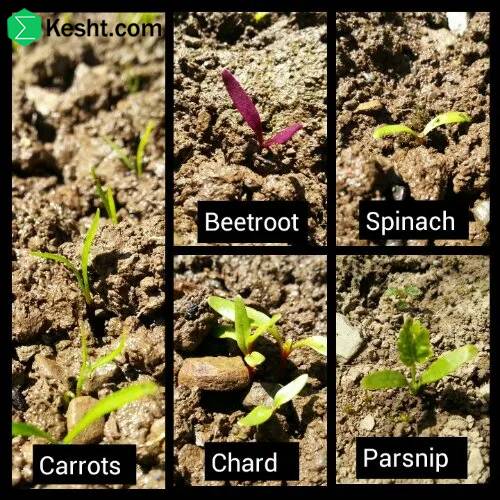
The global trade of fruit trees has expanded significantly in recent years, creating opportunities for nurseries and agricultural businesses. However, exporting live plants comes with unique challenges alongside its benefits. This article examines the key advantages and disadvantages of exporting fruit trees to help growers make informed decisions about international trade
If you are interested, it is recommended that you read the following article / article title:
Fruit Tree Importing Countries in the Middle East
https://ekesht.com/en/blog/fruit-tree-importing-countries-in-the-middle-east
Advantages of Exporting Fruit Trees
:Increased Revenue Opportunities
Access to higher-paying international markets where certain varieties are in demand
Ability to command premium prices for unique or disease-resistant cultivars
Diversified income streams beyond local market limitations
:Market Expansion
Ability to serve countries with unsuitable climates for growing certain species
Opportunity to introduce new varieties to regions lacking genetic diversity
Potential to establish long-term trade relationships with foreign buyers
:Utilization of Surplus Production
Monetize excess inventory that exceeds domestic demand
Reduce waste of unsold nursery stock
Optimize production capacity through larger-scale operations
:Competitive Advantages
Build international reputation as a quality supplier
Gain first-mover advantage with new cultivars in emerging markets
Access to foreign investment and agricultural development programs
Disadvantages of Exporting Fruit Trees
:Regulatory Challenges
Strict phytosanitary requirements that vary by country
Complex certification processes for plant health and traceability
Potential for entire shipments to be rejected due to minor compliance issues
:High Logistics Costs
Specialized packaging required to keep trees alive in transit
Expedited shipping needs to prevent plant stress or death
Customs clearance delays that can jeopardize plant health
:Biological Risks
Potential to unintentionally spread pests/diseases to importing countries
Quarantine requirement that may delay sales
Genetic contamination concerns in some markets
:Market Uncertainties
Currency fluctuations affecting profitability
Political instability in importing countries
Changing import regulations that may disrupt trade
If you are interested, it is recommended that you read the following article / article title:
The highest demand for seedling exports
https://ekesht.com/en/blog/the-highest-demand-for-seedling-exports
Key Considerations for Successful Exports
Mitigation Strategies
Invest in proper certifications (GAP, phytosanitary, etc.)
Develop relationships with import agencies in target markets -Use climate-controlled logistics for sensitive varieties
Maintain rigorous pest management programs
Diversify export markets to reduce risk
Emerging Opportunities
Growing demand for organic and heirloom varieties
Increasing interest in drought-resistant cultivars
New technologies in plant preservation during transit
Exporting fruit trees presents lucrative opportunities for growers to expand their markets and increase profits, but requires careful navigation of regulatory, logistical, and biological challenges. Successful exporters combine thorough preparation with adaptive strategies to overcome trade barriers. As global demand for diverse fruit varieties continues to grow, businesses that master the complexities of international plant trade stand to gain significant competitive advantages. For growers considering exports, starting with small test shipments to nearby markets can help build experience before expanding to more distant destinations. Consulting with agricultural export specialists and participating in trade programs can also smooth the path to successful international sales.