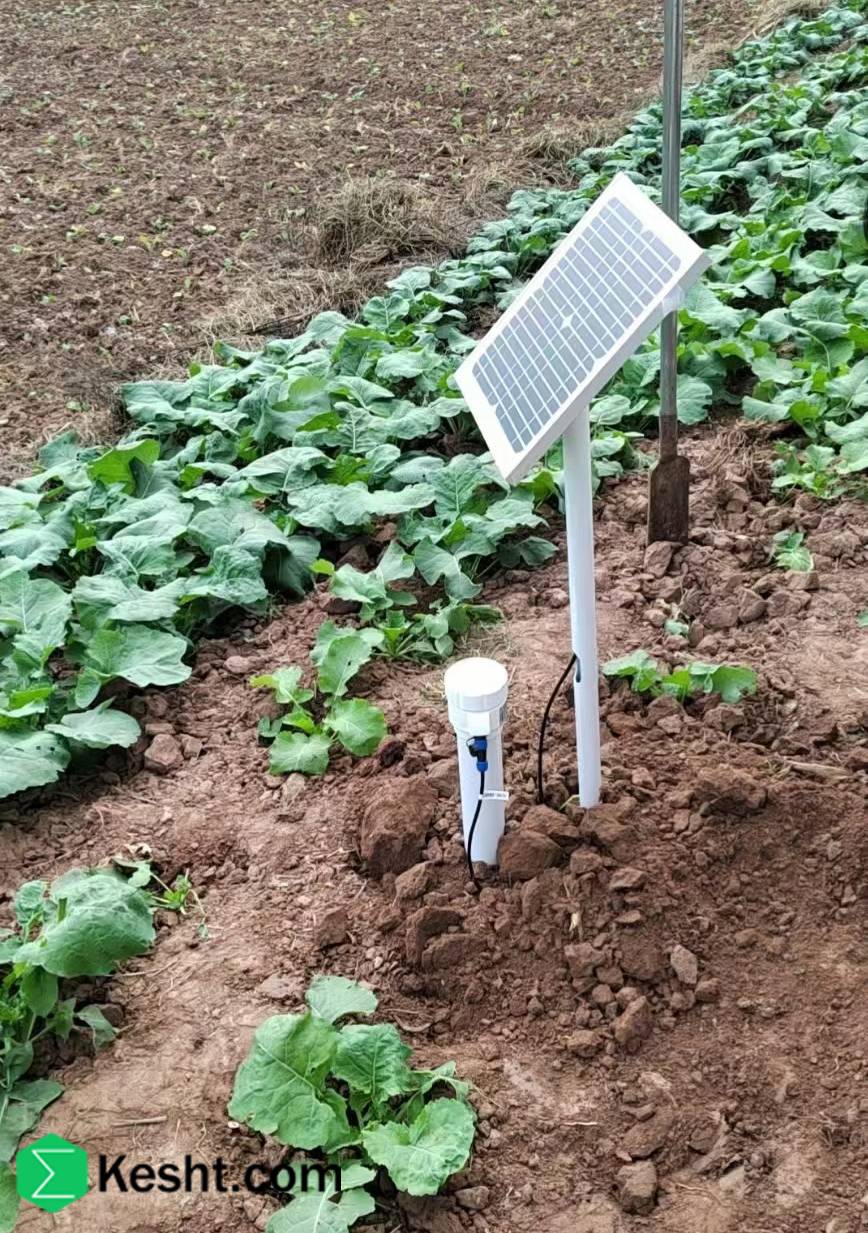
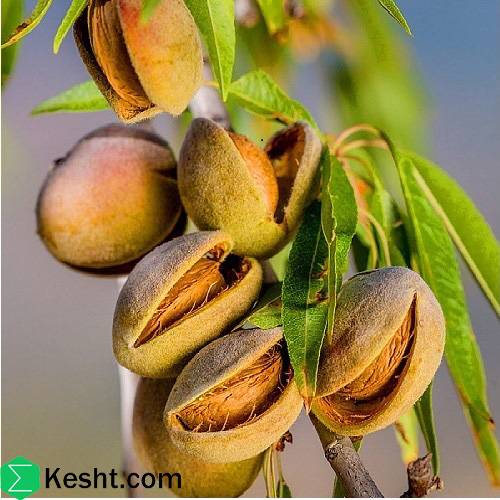
Almond tree (Prunus dulcis) is one of the most valuable and economical fruit trees in Iran and many countries around the world. In addition to its high nutritional value, almond kernels are also used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food processing industries, and for this reason, its planting and cultivation are very important.
Despite these advantages, almond trees are highly vulnerable to various pests and diseases. Fungal, bacterial and viral diseases, as well as sucking and chewing pests, can significantly reduce the yield of almond orchards. Accordingly, pest and disease management has become one of the main pillars of almond production.
Among the various control methods, chemical control is still one of the most common and fastest ways. However, experience has shown that the effectiveness of pesticides will only be sustainable if they are applied at the right time and with the right principles. Otherwise, not only will efficiency be reduced, but pest resistance, environmental damage, and increased costs will also occur.
This article will address the topic of when to spray almond trees in detail, examining the different stages of tree growth, pest life cycles, important diseases, and implementation considerations.
The Importance of Timing in Spraying
The timing of spraying almond trees is a determining factor in the success of pest control programs. Timely spraying can:
Prevent the initial establishment of pests and diseases.
Minimize damage at critical stages (germination, flowering, and fruit formation).
Reduce pesticide use and help maintain ecosystem health.
Prevent the development of drug resistance in pests and diseases.
Increase the economic performance of the orchard.
If spraying is done at the wrong time, the tree may be in a sensitive stage and the poison may not only be ineffective, but also directly damage the blossoms, leaves or fruits.
Key stages of almond tree growth and appropriate spraying
1. Dormancy period (December to March)
In this stage, the tree is leafless and in a state of rest. However, many pests and fungi remain in the soil as eggs, pupae or spores on the branches, trunk or fallen leaves.
Target pests and diseases: Aphid and mite eggs, sieve spot, brick leaf spot, bacterial canker.
Common pesticides: Volk oils (to destroy eggs and overwintering insects) and copper compounds (for fungal diseases).
Importance: This spraying serves as the basis of an annual program and if not done correctly, the likelihood of a pest outbreak in the spring will be much higher.
2. Bud swelling stage (March to April)
During this period, buds begin to awaken and the humid spring conditions can be a suitable environment for fungal growth.
Target diseases: brown spot, sieve, blossom rot.
Objective: Prevent initial bud contamination.
Important: Spraying should be done before spring rains so that the protective fungicide layer can form on the buds.
3. Flowering stage (April)
This period is very sensitive. Pollination is done by bees and improper use of pesticides can destroy pollinators and reduce yields.
- Recommendation: Avoid spraying under normal conditions.
- Exception: In case of severe disease outbreaks (such as blossom rot), use low-risk fungicides that are not harmful to bees.
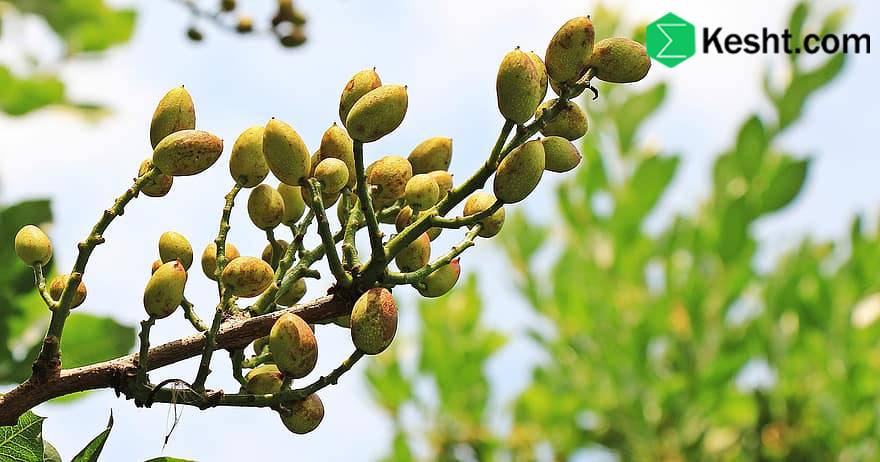
4. After petal fall and fruit formation (May)
This stage is economically very important, because sucking pests such as aphids, thrips and mites can quickly increase their population and cause great damage to young fruits.
Objective: Control pests that transmit viral diseases and prevent tree weakness.
Integrated management: Simultaneously with spraying, the use of natural enemies such as ladybugs is very effective.
5. Fruit growth period (summer)
As the fruit grows, chewing pests such as worms and moths become more important. Fungal diseases can also occur in the event of moisture and improper irrigation.
Measures: Install pheromone traps to track pests, use selective pesticides.
Implementation tip: Spray during cool hours (morning or evening) to prevent rapid evaporation of the solution and leaf burn.
6. After harvest (autumn)
This period is the last chance to reduce the pest population. Spraying at this time helps the tree enter the dormant season with less stress.
Common materials: Copper solutions to control fungal diseases of branches and leaves.
Importance: Reducing the burden of pests and diseases for the following year.
Important pests and diseases of almond trees and when to fight -Pests:
Almond green rot → spring and summer.
European red mite → early summer.
Aphids → summer.
Fruitworm → from fruit formation to harvest. -Diseases:
Screen spot → winter and early spring.
Bacterial canker → winter.
Blossom rot → early spring.
Brown spot → spring and summer.
Implementation and safety tips
Environmental conditions: - Suitable temperature: 15–25 ° C.
- Avoid strong winds and rain.
Equipment:
-The sprayer must be in good condition and calibrated.
-The particles must be sprayed evenly and cover all parts of the tree.
Personal safety:
-Use gloves, mask and goggles. -Wash the body and clothes thoroughly after work.
Product hygiene:
-Observe the Karnes period (time between the last spray and harvest). - Avoid using high-risk pesticides in the period close to harvest.
Environmental and economic considerations
Although spraying is an effective method, its excessive and incorrect use has negative consequences:
Contamination of soil and water resources.
Threat to the health of pollinators and natural enemies.
Increased production costs due to excessive use of pesticides.
When to Spray Almond Trees: A Comprehensive Guide to Pest and Disease Management

Related Articles