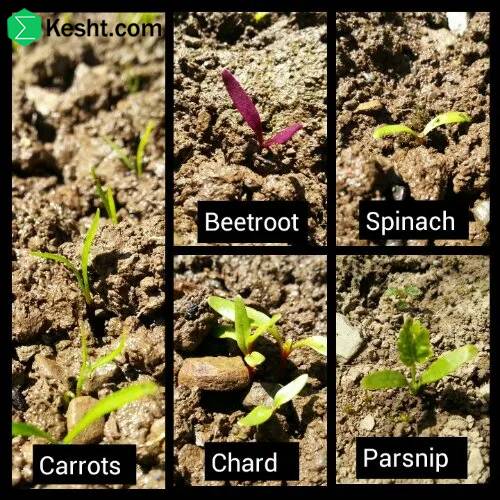
Selecting the right seedling is one of the key steps in modern agriculture that has a direct impact on the yield and quality of products. Given the climatic and geographical diversity in Iran, selecting seedlings must be done carefully and with attention to the specific conditions of each region. In this article, we will examine in more detail the important points in selecting the right seedling according to different regions and climates of Iran.
1. Understanding the different climates of Iran
Iran is divided into four main climates, each with its own characteristics and challenges:
1.1. Hot and dry climate
This climate includes the central and southern regions of the country, including Yazd, Kerman, and Fars.
Characteristics:
High temperatures: In summer, the temperature reaches more than 40 degrees Celsius.
Low rainfall: The average annual rainfall is between 100 and 200 millimeters.
Suitable seedlings:
Date (Phoenix dactylifera): This seedling is one of the most important agricultural crops in these areas due to its tolerance to heat and water shortage. Dates need 250 to 300 sunny days per year to bear fruit.
Apricot (Prunus armeniaca): This seedling is resistant to high summer temperatures and drought and requires limited irrigation. Apricots grow best at temperatures of 25 to 30 degrees Celsius.
Grapes (Vitis vinifera): Certain varieties of grapes are resistant to drought and high temperatures and can perform well in these areas. Grapes need a lot of sunlight and grow best in sandy or loamy soils.
1.2. Cold and mountainous climate
The northwestern regions and some northern regions such as Azerbaijan and Kurdistan fall into this category.
Characteristics:
Cold and frost: Temperatures drop below zero in the cold seasons and long-term frosts may occur.
Snowfall: Heavy snowfall is common in these areas and can help groundwater resources.
Suitable seedlings:
Apple (Malus domestica): This seedling is resistant to cold and frost and requires low temperatures to grow. Apples require soils with a medium pH (around 6-7) and good drainage.
Pear (Pyrus communis): This seedling is also resistant to cold and can grow well in sub-zero temperatures. Pears require soil moisture and regular irrigation.
Peach (Prunus persica): Some peach varieties are resistant to frost and can be grown in these areas. Peaches require well-drained soils and sufficient light.
1.3. Mediterranean climate
This climate includes the northern and western regions of the country such as Gilan and Mazandaran.
Characteristics:
High humidity: High rainfall and high relative humidity are characteristics of these areas.
Moderate temperatures: Temperatures in these areas usually range between 10 and 30 degrees Celsius.
Suitable seedlings:
Orange (Citrus sinensis): A seedling that is resistant to high humidity and rainfall and needs a lot of sunlight. Oranges need soils with a pH of 5.5 to 6.5 to grow.
Lemon (Citrus limon): This seedling needs plenty of water and humidity and grows well in these areas. Lemons need soils with organic matter and good drainage.
Kiwi (Actinidia deliciosa): A seedling that requires high humidity conditions that performs well in these areas. Kiwi needs indirect light and soils rich in organic matter.
1.4. Semi-arid climate
The western and eastern regions of the country fall into this category.
Features:
Variable temperatures: Temperature fluctuations are significant in these areas and temperatures may drop sharply at night.
Limited rainfall: Rainfall is typically less than 200 mm per year.
Suitable seedlings:
Almond (Prunus dulcis): A drought-resistant seedling that can perform well in these areas. Almonds require sandy, well-drained soils.
Pistachio (Pistacia vera): One of the main agricultural crops in these areas, which is resistant to water shortages and high temperatures. Pistachios require soils with a pH of 7 to 8.
Potato (Solanum tuberosum): Due to the climatic diversity, this crop can also be grown in semi-arid areas. Potatoes require rich soils and regular irrigation.
2. Important points in selecting seedlings
2.1. Soil investigation
Analysis of the soil and its pH can help in selecting the right seedling. Different soils have different characteristics that can affect seedling growth. For example:
Sandy soil: has excellent drainage but may lose moisture quickly.
Clay soil: has high water holding capacity but may not drain well.
2.2. Environmental conditions
Considering the temperature, humidity and rainfall in the area can be effective in selecting seedlings. For example, in areas with low rainfall, seedlings that are drought tolerant should be selected.
2.3. Local experience
Consulting with local farmers and reviewing their experience can provide valuable information in selecting seedlings. Experienced farmers can share key points about successful seedlings and local challenges.
2.4. Use resistant seedlings
Choosing seedlings that are resistant to diseases and pests is also of great importance. Seedlings that are resistant to diseases specific to the area can perform better and require less care. For example, seedlings resistant to fungal diseases in humid and rainy areas can have a great impact on reducing losses.
3. Conclusion
Choosing the right seedlings according to the different regions and climates of Iran requires careful consideration and sufficient knowledge of environmental conditions. By considering the points raised, farmers can choose seedlings that will lead to better performance and greater profitability.
Selecting the right seedling according to different regions and climates of Iran
Related Articles