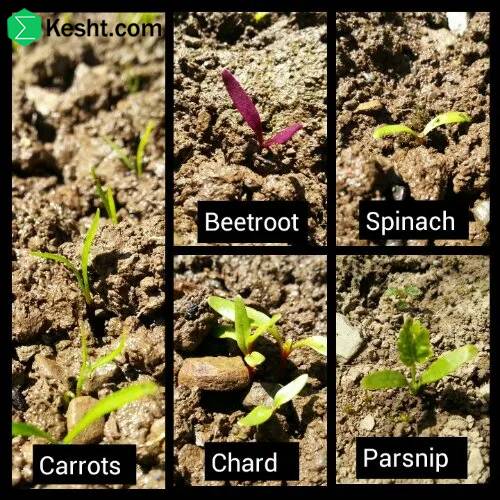
Deep Irrigation for seedling
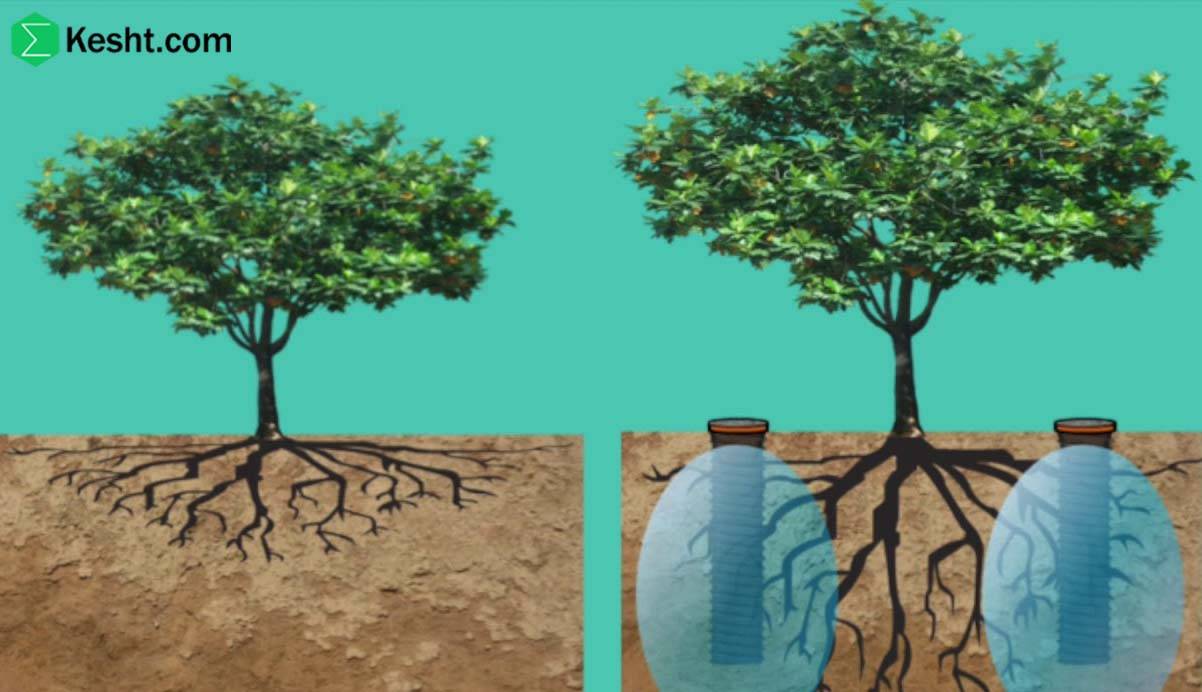
Deep irrigation is a method designed to meet the water needs of plants at deeper soil levels. This method is particularly useful in areas with high salinity or soils with low water retention capacity. Below are more details about deep irrigation:
Definition of Deep Irrigation for seedling:
Deep irrigation refers to supplying water to depths greater than the soil surface, allowing plant roots to access water. This method typically involves high-volume irrigation that penetrates deep into the soil.
If you are interested, it is recommended that you read the following article / article title:
A comprehensive guide to buying seedlings: key tips for choosing healthy, productive seedlings
https://ekesht.com/en/blog/a-comprehensive-guide-to-buying-seedlings
Benefits of Deep Irrigation for seedling:
Better Access to Water: Plants can access water stored at deeper levels, especially in drought conditions.
Reduced Salinity: Washing away accumulated salts at the soil surface reduces soil salinity.
Root Development: This method encourages roots to grow deeper in the soil, which can improve plant stability.
Reduced Evaporation: Deep irrigation helps decrease evaporation from the soil surface.
Methods of Deep Irrigation for seedling:
Drip Irrigation: Utilizing drip irrigation systems that deliver water directly to the plant roots and penetrate deep into the soil.
Subsurface Irrigation: In this method, pipes or underground tubes transport water to deeper soil levels.
High-Volume Irrigation: Providing a large volume of water at once to the soil for deeper infiltration.
Important Considerations in Deep Irrigation:
Timing: The timing of irrigation should allow the soil to absorb water and prevent runoff.
Water Quality: Using fresh and high-quality water is essential to avoid increasing soil salinity.
Soil Assessment: Before starting irrigation, the soil condition and its water retention capacity should be assessed.
Challenges:
Cost: Installing and setting up deep irrigation systems can be expensive.
Management: Requires careful management to avoid over-irrigation and problems such as soil saturation.
Deep irrigation is an effective method for meeting the water needs of plants, especially under challenging conditions. By appropriately selecting this method and paying attention to important factors, soil quality can be improved, and crop yields can increase.
Deep Drip Irrigation for seedling
Deep drip irrigation is an efficient and modern method for supplying water to plants through drip irrigation systems that deliver water directly to the roots. This method is particularly beneficial in sustainable agriculture and in areas with limited water resources. Below are more details about deep drip irrigation:
Definition of Deep Drip Irrigation:
Deep drip irrigation refers to the use of drip irrigation systems to supply water to deeper soil levels. This system delivers water to plant roots through underground pipes or drip emitters.
If you are interested, it is recommended that you read the following article / article title:
The best time to plant seedlings and check the soil
https://ekesht.com/en/blog/the-best-time-to-plant-seedlings-and-check-the-soil
Benefits of Deep Drip Irrigation:
Water Conservation: This method significantly reduces water consumption due to precise water distribution.
Reduced Salinity: By delivering water to deeper soil, accumulated salts at the surface are washed away.
Better Root Growth: Encourages roots to grow deeper in the soil, which can enhance plant stability and strength.
Reduced Evaporation: Since water reaches the roots directly, evaporation from the soil surface is minimized.
Components of Deep Drip Irrigation Systems:
Pipes and Drip Emitters: For uniform water distribution to the roots.
Pump: To pressurize water into the system.
Filters: To prevent suspended particles and organic materials from entering the system.
Controllers: To regulate the amount and timing of irrigation.
Important Considerations for Installation and Management:
Proper Design: The system design should ensure that water penetrates to the appropriate depth and reaches all roots.
Pressure Adjustment: Water pressure should be set to allow water to infiltrate the soil slowly and uniformly.
Regular Inspection: Regular checks are needed to prevent clogging of emitters and ensure proper operation.
Challenges:
Initial Costs: Installation and setup costs may be high.
Management Requirements: Requires precise management to adjust irrigation timing and amounts.
Deep drip irrigation is an effective method for supplying water to plants under various conditions. With proper design and management, this system can improve crop performance and conserve water resources.
How to Prevent Drip Emitter Clogging
If you are interested, it is recommended that you read the following article / article title:
Periodic soil testing
https://ekesht.com/en/blog/periodic-soil-testing
Preventing clogging of emitters in drip irrigation systems is crucial, as blockages can reduce irrigation efficiency and harm crops. Below are methods to prevent this issue:
Use of Filters:
Appropriate Filters: Installing filters at the system's inlet can separate suspended particles, dirt, and organic materials that may cause emitter clogging.
Type of Filter: Screen filters or disc filters are usually the best options.
Regular Cleaning:
Periodic Inspection: Regularly check the system and clean the emitters and pipes.
Flushing: If deposits are present, flush the emitters with water or cleaning solutions.
Use of Quality Water:
Water Source: Use water of suitable quality for irrigation. Contaminated water or water with suspended particles can lead to emitter clogging.
Water Treatment: If necessary, use water treatment systems to improve quality.
Pressure Adjustment:
Appropriate Pressure: Ensure that the water pressure in the system is within the suitable range. Excess pressure can damage emitters and cause blockages.
Pressure Control: Use pressure controllers to adjust and maintain proper pressure.
Use of Anti-Clogging Emitters:
Special Emitters: Utilize emitters designed to prevent clogging, which typically have specific designs to avoid particle accumulation.
Reduce Organic Materials:
Management of Organic Materials: Reducing the use of organic fertilizers or materials in irrigation can help decrease deposits.
Use of Compost: If using compost, ensure that it is of high quality and well-treated.
Proper Irrigation:
Regular Irrigation: Regular and adequate irrigation can help prevent the accumulation of salts and other materials in the system.
Irrigation Management: Employ deep and appropriate irrigation to avoid salt accumulation and excess materials.
By following these methods, you can reduce the risk of emitter clogging and increase the efficiency of your drip irrigation system. Regular management and monitoring of the system can help maintain optimal performance.
If you are interested, it is recommended that you read the following article / article title:
What types of fertilizers are suitable for soil amendment?
https://ekesht.com/en/blog/what-types-of-fertilizers-are-suitable-for-soil-amendment
Is Using Acid to Clean Emitters Recommended?
Using acid to clean emitters can be effective, but it should be done with caution. Here are important considerations to keep in mind:
Type of Acid:
Mild Acids: Using mild acids like citric acid or vinegar can be a suitable option. These acids are generally safer and do not damage plastic materials.
Strong Acids: Avoid using strong acids such as sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, as they can damage the emitters and pipes.
Dilution and Cleaning Time:
Dilution: If you use acid, make sure to dilute it and avoid high concentrations.
Contact Time: The contact time with the acid should be limited. Usually, a few minutes is sufficient to dissolve deposits.
Rinsing:
Thorough Rinsing: After using acid, thoroughly rinse the emitters and pipes with water to ensure no acid residue remains.
Inspection: After rinsing, check the system to ensure that no damage has occurred to the emitters.
Safety:
Gloves and Goggles: Always use gloves and safety goggles when working with acid.
Ventilation: Perform the work in a well-ventilated area.
Alternative Methods:
Non-Acidic Solutions: For cleaning, you can use non-acidic solutions or natural cleaners that are effective enough and pose less risk.
Using acid to clean emitters can be effective, but it should be done carefully with safety considerations in mind. Whenever possible, opt for non-acidic and milder methods to prevent damage to the irrigation system.
Examples of Non-Acidic Solutions
Here are some examples of non-acidic solutions that can be used to clean emitters and irrigation systems:
Vinegar and Water Solution:
Mix: 1 part vinegar (white or apple cider) with 3 parts water.
Use: This solution acts as a mild cleaner and can dissolve mineral deposits.
Baking Soda Solution:
Mix: 1 tablespoon of baking soda in 1 liter of warm water.
Use: Baking soda can help eliminate odors and deposits and is safe to use.
Liquid Soap Solution:
Mix: A few drops of liquid soap in warm water.
Use: The soap solution can aid in cleaning and removing deposits.
Salt Water Solution:
Mix: 1 tablespoon of salt in 1 liter of warm water.
Use: Salt can help dissolve some deposits and acts as a natural cleaner.
Special Cleaning Powder:
Use of Commercial Powders: Some commercial cleaning powders are available for irrigation systems that are generally safe and effective.
If you are interested, it is recommended that you read the following article / article title:
Solid organic fertilizers
https://ekesht.com/en/blog/solid-organic-fertilizers
Isopropyl Alcohol Solution:
Mix: Diluted isopropyl alcohol with water.
Use: This solution can help eliminate bacteria and deposits.
Important Notes:
Thorough Rinsing: After using any of these solutions, be sure to rinse the emitters thoroughly with water.
Material Check: Before use, ensure that the materials used are compatible with the plastics in the irrigation system.
By using these non-acidic solutions, you can clean your irrigation system without the risk of damaging it.
We are the “ekesht” platform — a subsidiary of Samin Atlas Iranians and the only official exporter of BlueLabel seedlings in Iran
Why Blue Label?
Because the world only trusts these seedlings!
Ordinary seedlings (without labels or other labels), even if one of them is infected, can destroy your entire garden — without you realizing it!
But the advantage of Blue Label seedlings:
✅Each of them has a global barcode
✅Tested in advanced laboratories
✅Free from any viruses and microbes
✅The only seedlings that are allowed to be legally exported!
This is important for you if:
- You want to build a garden that is productive and hassle-free
- You are looking for a long-term investment in gardening
- You want to start without stress, without losses, without surprises!
Blue Label seedlings = peace of mind
Because when the seedlings are healthy, the garden stays healthy — and real profits come!
Contact us now — before a random seedling destroys your garden!
Healthy Seedlings = Fruitful Garden = Smart Investment
And that’s exactly what we do at ekesht.
ekesht platform (with fifteen years of practical and successful trade experience with Russia, Kazakhstan, Iraq, China, Turkmenistan, Turkey, etc.) is ready to cooperate with people active in the field of agriculture.
For more information and additional information, please contact us via social media, phone call or email
Phone number:
Email:
Social media address: